Bun 内置了一个快速、Jest 兼容的测试运行器。测试使用 Bun 运行时执行,并支持以下功能。
- TypeScript 和 JSX
- 生命周期钩子
- 快照测试
- UI 和 DOM 测试
- 使用
--watch的观察模式 - 使用
--preload的脚本预加载
Bun 的目标是与 Jest 兼容,但并非所有功能都已实现。要跟踪兼容性,请参阅此跟踪问题。
运行测试
bun test测试以 JavaScript 或 TypeScript 编写,使用类似 Jest 的 API。有关完整文档,请参阅编写测试。
import { expect, test } from "bun:test";
test("2 + 2", () => {
expect(2 + 2).toBe(4);
});
运行器递归搜索工作目录中与以下模式匹配的文件
*.test.{js|jsx|ts|tsx}*_test.{js|jsx|ts|tsx}*.spec.{js|jsx|ts|tsx}*_spec.{js|jsx|ts|tsx}
您可以通过向 bun test 传递额外的位置参数来筛选要运行的_测试文件_集。任何路径与其中一个筛选器匹配的测试文件都将运行。通常,这些筛选器将是文件或目录名称;目前不支持 glob 模式。
bun test <filter> <filter> ...要按_测试名称_筛选,请使用 -t/--test-name-pattern 标志。
# run all tests or test suites with "addition" in the namebun test --test-name-pattern addition当没有测试匹配筛选器时,bun test 以代码 1 退出。
要在测试运行器中运行特定文件,请确保路径以 ./ 或 / 开头,以将其与筛选器名称区分开来。
bun test ./test/specific-file.test.ts测试运行器在单个进程中运行所有测试。它加载所有 --preload 脚本(有关详细信息,请参阅生命周期),然后运行所有测试。如果测试失败,测试运行器将以非零退出代码退出。
CI/CD 集成
bun test 支持各种 CI/CD 集成。
GitHub Actions
bun test 自动检测它是否在 GitHub Actions 中运行,并将直接向控制台输出 GitHub Actions 注释。
除了在工作流中安装 bun 并运行 bun test 之外,不需要其他配置。
如何在 GitHub Actions 工作流中安装 bun
要在 GitHub Actions 工作流中使用 bun test,请添加以下步骤
jobs:
build:
name: build-app
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Install bun
uses: oven-sh/setup-bun@v2
- name: Install dependencies # (assuming your project has dependencies)
run: bun install # You can use npm/yarn/pnpm instead if you prefer
- name: Run tests
run: bun test
从那里,您将获得 GitHub Actions 注释。
JUnit XML 报告 (GitLab 等)
要将 bun test 与 JUnit XML 报告器一起使用,您可以将 --reporter=junit 与 --reporter-outfile 结合使用。
bun test --reporter=junit --reporter-outfile=./bun.xml这将像往常一样继续输出到 stdout/stderr,并在测试运行结束时将 JUnit XML 报告写入给定路径。
JUnit XML 是一种在 CI/CD 流水线中报告测试结果的流行格式。
超时
使用 --timeout 标志指定_每个测试_的超时时间(毫秒)。如果测试超时,它将被标记为失败。默认值为 5000。
# default value is 5000bun test --timeout 20并发测试执行
默认情况下,Bun 在每个测试文件中按顺序运行所有测试。您可以启用并发执行以并行运行异步测试,从而显著加快具有独立测试的测试套件。
--concurrent 标志
使用 --concurrent 标志在其各自的文件中并发运行所有测试
bun test --concurrent启用此标志后,除非明确标记为 test.serial,否则所有测试都将并行运行。
--max-concurrency 标志
使用 --max-concurrency 标志控制同时运行的最大测试数量
# Limit to 4 concurrent testsbun test --concurrent --max-concurrency 4
# Default: 20bun test --concurrent这有助于在运行许多并发测试时防止资源耗尽。默认值为 20。
test.concurrent
标记单个测试以并发运行,即使未使用 --concurrent 标志
import { test, expect } from "bun:test";
// These tests run in parallel with each other
test.concurrent("concurrent test 1", async () => {
await fetch("/api/endpoint1");
expect(true).toBe(true);
});
test.concurrent("concurrent test 2", async () => {
await fetch("/api/endpoint2");
expect(true).toBe(true);
});
// This test runs sequentially
test("sequential test", () => {
expect(1 + 1).toBe(2);
});
test.serial
即使启用了 --concurrent 标志,也强制测试按顺序运行
import { test, expect } from "bun:test";
let sharedState = 0;
// These tests must run in order
test.serial("first serial test", () => {
sharedState = 1;
expect(sharedState).toBe(1);
});
test.serial("second serial test", () => {
// Depends on the previous test
expect(sharedState).toBe(1);
sharedState = 2;
});
// This test can run concurrently if --concurrent is enabled
test("independent test", () => {
expect(true).toBe(true);
});
// Chaining test qualifiers
test.failing.each([1, 2, 3])("chained qualifiers %d", input => {
expect(input).toBe(0); // This test is expected to fail for each input
});
重新运行测试
使用 --rerun-each 标志多次运行每个测试。这对于检测不稳定或非确定性测试失败很有用。
bun test --rerun-each 100随机化测试执行顺序
使用 --randomize 标志以随机顺序运行测试。这有助于检测依赖于共享状态或执行顺序的测试。
bun test --randomize使用 --randomize 时,用于随机化的种子将显示在测试摘要中
bun test --randomize# ... test output ...
--seed=12345
2 pass
8 fail
Ran 10 tests across 2 files. [50.00ms]使用 --seed 可重现随机顺序
使用 --seed 标志为随机化指定一个种子。这允许您在调试依赖于顺序的失败时重现相同的测试顺序。
# Reproduce a previous randomized runbun test --seed 123456--seed 标志意味着 --randomize,因此您无需同时指定两者。使用相同的种子值将始终产生相同的测试执行顺序,从而更容易调试由测试相互依赖性引起的间歇性失败。
使用 --bail 退出
使用 --bail 标志在预定数量的测试失败后提前中止测试运行。默认情况下,Bun 将运行所有测试并报告所有失败,但有时在 CI 环境中,为了减少 CPU 使用率,提前终止是更可取的。
# bail after 1 failurebun test --bail
# bail after 10 failurebun test --bail=10Watch 模式
与 bun run 类似,您可以将 --watch 标志传递给 bun test 以监视更改并重新运行测试。
bun test --watch生命周期钩子
Bun 支持以下生命周期钩子
| 钩子 | 描述 |
|---|---|
beforeAll | 在所有测试运行之前运行一次。 |
beforeEach | 在每个测试运行之前运行。 |
afterEach | 在每个测试运行之后运行。 |
afterAll | 在所有测试运行之后运行一次。 |
这些钩子可以在测试文件中定义,也可以在单独的文件中定义,并使用 --preload 标志进行预加载。
$ bun test --preload ./setup.ts
有关完整文档,请参阅测试 > 生命周期。
模拟
使用 mock 函数创建模拟函数。
import { test, expect, mock } from "bun:test";
const random = mock(() => Math.random());
test("random", () => {
const val = random();
expect(val).toBeGreaterThan(0);
expect(random).toHaveBeenCalled();
expect(random).toHaveBeenCalledTimes(1);
});
或者,您可以使用 jest.fn(),它的行为完全相同。
import { test, expect, mock } from "bun:test";
import { test, expect, jest } from "bun:test";
const random = mock(() => Math.random());
const random = jest.fn(() => Math.random());有关完整文档,请参阅测试 > 模拟。
快照测试
bun test 支持快照。
// example usage of toMatchSnapshot
import { test, expect } from "bun:test";
test("snapshot", () => {
expect({ a: 1 }).toMatchSnapshot();
});
要更新快照,请使用 --update-snapshots 标志。
bun test --update-snapshots有关完整文档,请参阅测试 > 快照。
UI & DOM 测试
Bun 兼容流行的 UI 测试库
有关完整文档,请参阅测试 > DOM 测试。
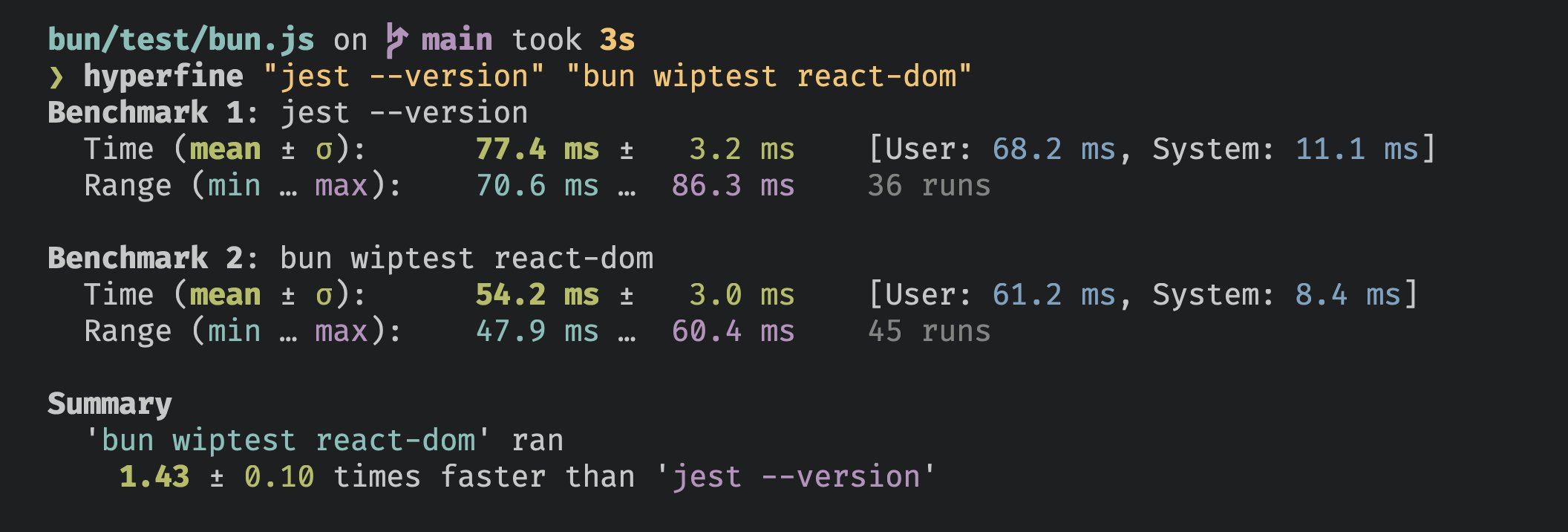
性能
Bun 的测试运行器速度很快。
AI 代理集成
将 Bun 的测试运行器与 AI 编码助手一起使用时,您可以启用更安静的输出,以提高可读性并减少上下文噪音。此功能最大程度地减少了测试输出的冗长性,同时保留了必要的失败信息。
环境变量
设置以下任何环境变量以启用 AI 友好的输出
CLAUDECODE=1- 用于 Claude CodeREPL_ID=1- 用于 ReplitAGENT=1- 通用 AI 代理标志
行为
当检测到 AI 代理环境时
- 仅详细显示测试失败
- 通过、跳过和待办测试指示器被隐藏
- 摘要统计数据保持不变
# Example: Enable quiet output for Claude CodeCLAUDECODE=1 bun test
# Still shows failures and summary, but hides verbose passing test output此功能在 AI 辅助开发工作流中特别有用,其中减少输出冗长性可以提高上下文效率,同时保持对测试失败的可见性。